Storage Equipment
Storage equipment used for holding or buffering materials over a period of time.
The most common reason for storing a product allows the other elements of production to operate more efficiently on a per-unit basis because the fixed costs associated with utilizing the element can be spread over more products; e.g., storing up to a truckload of product in a facility reduces the per-unit costs of shipping; and buffering or storage of WIP enables batch production which reduces the per-unit setup costs.
Other potential reasons for storage include: time bridging—allows product to be available when it is needed (e.g., storing spare machine parts at the facility); processing—for some products (e.g., wine), storage can be considered as a processing operation because the product undergoes a required change during storage; and securing—e.g., nuclear waste storage.
Below is the various types of storage equipments used in various warehouse.
1. Selective Pallet Rack
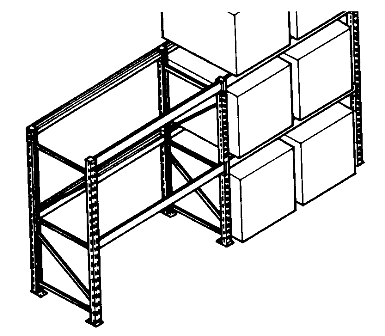
Information:
1. Selective Pallet Rack

Information:
- Most popular type of storage rack.
- Pallets are supported between load-supporting beams
- Special attachments and decking can be used to make the racks capable of supporting other types of unit loads besides pallets (e.g., coils, drums, skids).
- Selective racks can be used for the following types of storage:
- Standard—single-deep storage using a counterbalanced lift truck.
- Narrow-Aisle—storage using a narrow-aisle lift truck.
- Deep-Reach—greater than single-deep storage (typically double-deep storage).
- Allow a lift truck to enter the rack from either side to pick up or pull out pallets.
- Loads are supported by rails attached to upright frames.
- Lift trucks are driven between uprights to reach pallets.
- This is done because pallets can slide backwards on a continuous rail.
- It's open at both ends, allowing first-in, first-out storage (FIFO).
Drive Through FIFO
- Free access from both sides allows materials to be stored from one end and retrieved from the other.
- Used where there is expiration dated material or wherever shelf life is of major concern.
3. Drive-In Rack
- Ultimate in high-density storage.
- No other form provides more storage capacity per square foot of room than drive-in.
- A viable alternative to expanding one’s facility.Provides a very low cost yet efficient means of high volume storage.
- Offer the same storage density as drive-in & drive-through racks but greater selectivity.
- All loads are stored and retrieved from the aisle.
- Loads in each lane rest on a cart on a rail that slopes gently toward the front.
- When a new load is deposited into a lane, it ‘pushes back’ the one already at the face and all those behind.
- Then, when that load is picked, the contents of the lane all move gently forward again, hence the term "push back rack".
- Loads are supported by cantilever "arms".
- Used to store long loads (e.g., bar stock, pipes, lumber).
- Similar to pallet racks, except the front upright beams and the front supporting beams are eliminated.
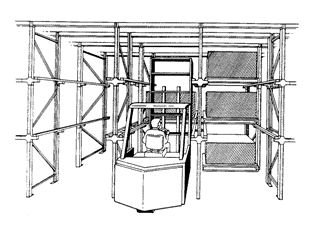
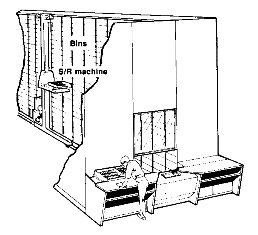
Consists of an integrated computer-controlled system that combines the storage medium, transport mechanism, and controls with various levels of automation for fast and accurate random storage of products and materials.
Storage/retrieval (S/R) machine in an AS/RS operates in narrow aisle, serving rack slots on both sides of aisle; can travel in horizontal (along the aisle) and vertical (up and down a rack) directions at same time
Advantages:
- Fewer material handlers,
- Better material control (including security)
- Efficient use of storage space.
Disadvantages:
- High capital and maintenance costs
- Difficult to modify.
- Used to store/retrieve loads that are palletized or unitized and weigh over 500 lbs.
- Stacking heights up to 130 ft. high,
- Most ranging from 60 to 85 ft. high; 5 to 6 ft. wide aisles
- Single- or double-deep storage racks
- Used to store/retrieve small parts and tools that can be stored in a storage bin or drawer.
- End-of-aisle order picking and replenishment.
- Stacking heights range from 12 to 20 ft.
- Bin capacities range from 200 to 750 lbs.
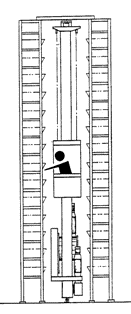
Man-On-Board AS/RS
- Used for in-aisle picking.
- Operator picks from shelves, bins, or drawers within the storage structure.
- Manual or automatic control
7. Mezzanine
- Inexpensive means of providing additional storage or office space.
- Makes use of clear space over activities not requiring much headroom (e.g., restrooms, block storage, etc.).
- At least 14 ft. of clear space is needed for a mezzanine.
Information:
- Loads are supported on an incline to enable gravity-based movement of the loads within the rack (via, e.g., a gravity roller conveyor)
- Loaded at the higher end.
- Unloaded at the lower end (FIFO)
Sources:
http://www.ise.ncsu.edu/kay/mhetax/StorEq/index.htm
http://estore.sjf.com/sjf.nsf/vwHelp/Drive-In+&+Drive-Thru+Rack?OpenDocument
http://conceptstorage.com/push_back_racking.html
http://www.mezzanine.co.uk/
http://www.ise.ncsu.edu/kay/mhetax/StorEq/index.htm
http://estore.sjf.com/sjf.nsf/vwHelp/Drive-In+&+Drive-Thru+Rack?OpenDocument
http://conceptstorage.com/push_back_racking.html
http://www.mezzanine.co.uk/